Implementation of image processing for the evaluation of tar spot (Phyllachora maydis) in corn (Zea mays)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.28940/terra.v40i0.1066Keywords:
doses, leaf, resistant, silicion, susceptibleAbstract
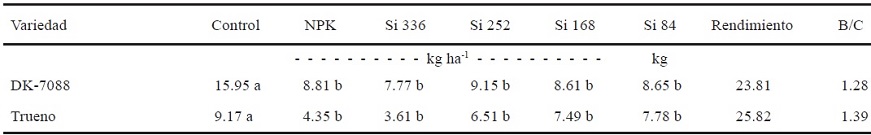
The disease known as tar spot (Phyllachora maydis) af fects corn (Zea mays). It causes lesions on the leaves that, when progressing, can cause the death of the plant. There are dif ferent methods to assess the progress of a disease in plants. Visual assessment scales are generally used; however, their use is quite subjective. Image processing has been used in recent times as an alternative for the evaluation of plant diseases. This alternative avoids bias and error during evaluations. The objective of this experiment was to use the Leaf Doctor cell phone application as an alternative to the evaluation of the disease caused by P. maydis. For the experiment, a completely randomized block design was used. Three varieties of corn were planted and the level of tolerance to tar spot was evaluated when treated with dif ferent doses of silicon. The most resistant variety to the disease was INIAP-551. The dif ferent doses of silicon do not reduce the disease; however, it was possible to determine an increase in the production of corn in doses of silicon of 252 kg ha-1. The results indicate that the program can be considered as an ef f icient alternative to evaluate the development of the disease known as tar spot due to the high correlation with the visual assessment scale (R2: 0.77-0.94).
Downloads
Publication Facts
Reviewer profiles N/A
Author statements
- Academic society
- Terra Latinoamericana
- Publisher
- Mexican Society of Soil Science, C.A.