Foliar Fertilization of Nano-selenium and its Ef fects on Bioactive Compounds and Enzymatic Activity in Lettuce
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.28940/terra.v42i0.1939Keywords:
antioxidants, biofortification, Lactuca sativa L., nanoparticles, nanotechnologyAbstract
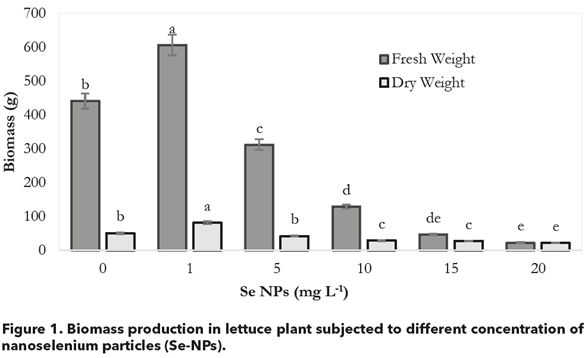
Selenium (Se) an oligoelement for mammals is not considered essential in plant fertilization programs. Its deficiency af fects almost one million persons, making it a world health problem and nano-biofortification of cultivation is a strategy to attenuate it. Thus, this study determines the foliar selenium nanoparticles (Se-NPs) application ef fects on yield, enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidants, and their accumulation in lettuce. Therefore, six applications of dif ferent Se-NPs concentrations: 0, 1, 5, 10, 15, and 20 mg L-1 were considered. The results showed that the high doses decrease yield, enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidants but increase Se concentration in lettuce leaves. The recommended dosage here is of 1 mg L-1 for biomass production and 10 mg L-1 for bioactive compounds and enzymatic activity. The recommended daily consumption of lettuce biofortified with 1 mg of Se-NPs (100 g) provides the recommended daily consumption in adults. Thus, the Se-NPs application is an alternative to increase Se concentration and bioactive compounds in lettuce to influence positively, human nutrition af ter its consumption.
Downloads
Publication Facts
Reviewer profiles N/A
Author statements
- Academic society
- Terra Latinoamericana
- Publisher
- Mexican Society of Soil Science, C.A.