Indole-3-acetic acid Acid Producing and Phosphorus and Potassium Solubilizing Bacteria as Growth Promoters in Oryza sativa L.
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.28940/terralatinoamericana.v43i.1969Keywords:
biofertilization, stimulants, PGPR, solubilization, sustainabilityAbstract
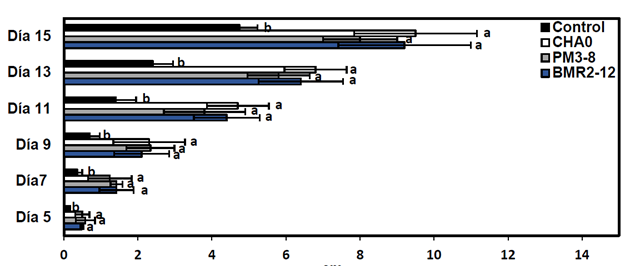
The rice has economic relevance on a global scale, and the application of agrochemicals has a negative impact on soil fertility and the environment. The objective of the research was to evaluate P and K solubilizing, ındole-3-acetic acid producing and growth promoting bacteria in rice (Oryza sativa L). The work was carried out in the Molecular Microbiology laboratory of the Universidad Técnica Estatal de Quevedo (UTEQ), Campus “La María”. A selection of nine rhizobacteria were isolated and molecularly characterized for IAA quantification and biochemical tests (N and K solubilization). The phytohormone-producing and nutrient solubilizing strains were applied and evaluated on root development in rice for 15 days. From the last experiment, the best strain was chosen for cell multiplication in bioformulations
and application together with fertilizers in plants. The application of Enterobacter asburiae BA4-19, Pseudomonas protegens CHA0, Serratia Marcescens PM3-8 and Acinetobacter calcoaceticus BM2-12 had hiould be used to improve crop yield and productivity.gh relative ef ficiency in solubilization of K and P. At 72 h, A. calcoaceticus BMR 2-12 produced higher AIA (17.9 μg mL-1). P. protegens CHA0 increased radicle length (9.50 cm). BIO-IMPULSE + UREA and BIO-IMPULSE + UREA showed greater plant height and root length of (71.7 and 27.0 cm). The application of BIO-IMPULSE with fertilizer showed higher leaf color intensity. It is concluded that rhizobacterial bioformulates It is concluded that rhizobacterial bioformulates could be used to improve crop yield and productivity.
Downloads
Publication Facts
Reviewer profiles N/A
Author statements
- Academic society
- Terra Latinoamericana
- Publisher
- Mexican Society of Soil Science, C.A.