Symbiotic Interaction Between Common Bean Genotypes and (Rhizobium spp.) Strains
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.28940/terra.v43i.1065Keywords:
multivariate analysis, factorial design, wild and cultivated forms, Phaseolus vulgaris L., native rhizobiaAbstract
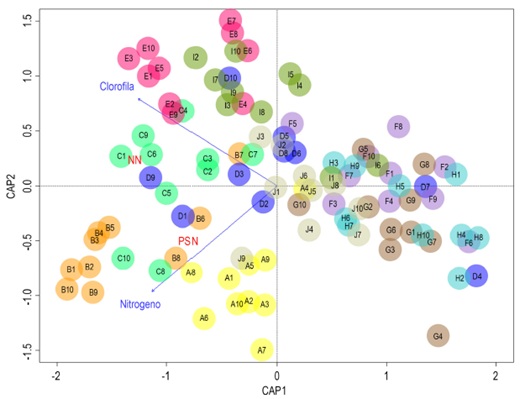
The legume-Rhizobium association is a high-ef ficiency process in biological nitrogen fixation that can supply up to 90% of the nitrogen needed in some species. To evaluate the symbiotic response of 10 cultivated and wild bean genotypes inoculated with 10 strains of Rhizobium isolated from domesticated and wild bean nodules, seedlings were grown and inoculated under greenhouse conditions in Zapopan, Jalisco, Mexico. At the beginning of the bean flowering, the variables associated with atmospheric nitrogen fixation were recorded: number of nodules (NN), dry weight of nodules (PSN), percentage of total nitrogen in the stem (NT) and chlorophyll content in the leaves (CL) in SPAD units. Multivariate analysis detected dif ferences for bean genotypes, Rhizobium strains, and for genotype × strain interaction. Cultivated bean genotypes generally outperformed wild bean genotypes in their response to the recorded variables. Similarly, isolates from cultivated beans were generally better than those from wild beans. The circular dendrogram separated the genotype-strain binomials first by gene pools of Andean and Mesoamerican beans, second by domesticated and wild bean forms, and third within each of the forms. The graph of the canonical analysis of principal coordinates showed a positive interaction of the cultivated bean-strains binomials with the four variables studied. The positive interactions of P Saltillo and Peruano 16 in NT and PSN in symbiosis with most of the strains stand out; of G Zarco in NN in symbiosis with six of the rhizobia; the interaction of Apetito in CL with six of the strains; the combinations of P Saltillo, Peruano 16 and G Zarco with the RhGz2 strain in the NT variable.
Downloads
Publication Facts
Reviewer profiles N/A
Author statements
- Academic society
- Terra Latinoamericana
- Publisher
- Mexican Society of Soil Science, C.A.