Evaluación morfoagronómica de plantas de lechuga (Latuca sativa L) cultivadas en acuaponia y con aplicación de quitosano
Efecto del quitosano en un sistema acuaponico
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.28940/terra.v42i0.1811Palabras clave:
bioestimulante, parámetros productivos, rendimientoResumen
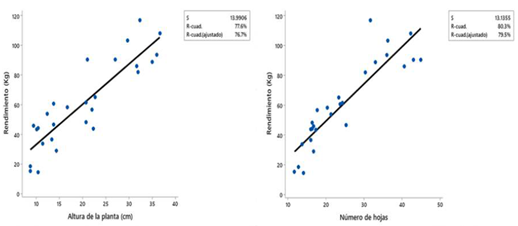
Los bioestimulantes como el quitosano en la agricultura tradicional han demostrado su eficacia para promover el crecimiento y desarrollo de las plantas, así como protegerlas de enfermedades, sin embargo, en sistemas de producción acuapónicos su efecto no está documentado, por ello el objetivo del presente trabajo fue determinar el efecto de la concentración de quitosano (0, 500 y 1000 mg.L) en tres variedades de lechuga (Grandes Lagos, Regina 500 y Red Rock), sobre los parámetros de producción de lechuga y la presencia de enfermedades en un sistema circular de acuaponia. Bajo un arreglo factorial de 3x3 el quitosano fue aplicado mediante aspersión a los 10 y 45 días después del trasplante. Se utilizó una análisis de varianza y comparación de medias con la prueba de Tukey para el efecto de la variedad, y polinomios ortogonales para el efecto de la concentración de quitosano, y un análisis de correlación y regresión para determinar la relación entre el rendimiento y la altura y el número y longitud de las hojas. Los resultados demuestran que las variables número de hojas, longitud de la raíz, peso de la planta, longitud de la hoja, altura de la planta y rendimiento, se incrementan conforme se aumenta la dosis de quitosano. La variedad Red Rock superó a las variedades Regina 500 y Grandes Lagos. No se detectó la presencia de insectos ni enfermedades. Se concluye que el quitosano favorece el crecimiento, desarrollo y rendimiento de la planta de lechuga en un sistema circular de acuaponía, sobre todo con dosis de 1000 mg.L de quitosano, y que respecto a estas mismas variables, la variedad Red Rock supera a las variedades Regina 500 y Grandes Lagos.
Descargas
Publication Facts
Reviewer profiles N/D
Author statements
- Academic society
- Terra Latinoamericana