Characterization of Microorganisms with Biotechnological Potential Isolated from Chemically and Organically Fertilized Agricultural Soils
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.28940/terralatinoamericana.v43i.2233Keywords:
soil contamination, herbicides, pesticides, remediation, solubilisationAbstract
Agricultural soil degradation is a global issue that negatively impacts productivity. Microorganisms with biotechnological potential play crucial roles in the remediation of contaminated soils and the enhancement of soil fertility. The research was conducted in the Microbiology laboratory of the Universidad Técnica Estatal de Quevedo with the objective of characterizing microorganisms with biotechnological potential isolated from agricultural soils fertilized with chemical and organic fertilizers under controlled conditions. The variables evaluated were pH, colony forming units (CFU) ml-1, and optical density, hypocotyl length, vigor index, germination percentage
and germination index. The results indicate that strains isolated from contaminated
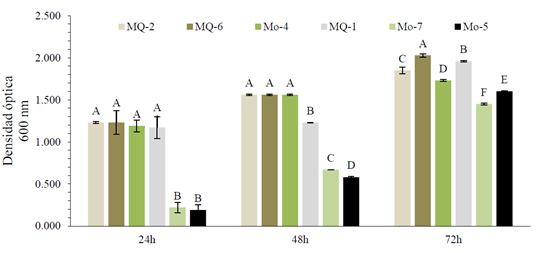
soil exhibit a higher microbial load, ranging from 7.40×106 to 2.58×108 CFU g-1. Strain Mo-7 showed tolerance to aluminum sulfate and phosphate solubilization activity, and MQ-6 showed high capacity to solubilize urea, phosphate and tolerance to Al2(SO4)3. Turbidity with pendimentalin, MQ-6 reached the highest optical density at 72 hours (2.03). The pH analysis in the presence of Al2(SO4)3, MQ-6 was higher (8.11). In cell concentration with Al2(SO4)3, MQ-6 maintained 8.80E+10 CFU ml-1. In vitro phytotoxicity with pendimentalin and Al2(SO4)3 on Oryza sativa seeds, MQ-6 achieved 100% germination, root length 6.83 cm and vigor index of 82.50. With Al2(SO4)3, MQ-6 achieved 100% germination, hypocotyl length 23.50 cm and high vigor index (303.00). These strains demonstrated their potential to biotransform soil-toxic molecules thereby promoting agricultural sustainability through bioremediation processes.
Downloads
Publication Facts
Reviewer profiles N/A
Author statements
- Academic society
- Terra Latinoamericana
- Publisher
- Mexican Society of Soil Science, C.A.
References
Acevedo, I; Sánchez, A; Mendoza, B. 2021. Evaluación del nivel de degradación del suelo en dos sistemas productivos en la depresión de Quíbor. II. Calidad del suelo. Bioagro 33(2):127-134
Ahmad, S., Ahmad, H. W., & Bhatt, P. (2022). Microbial adaptation and impact into the pesticide’s degradation. Archives of Microbiology, 204(5), 288.
Al-Masoodi, I. H., Al-Rubaye, A. F. M., & Hussein, H. J. (2023). Isolation and diagnosis of the fungi associated with maize seeds collected from local markets in Karbala, Iraq. Caspian Journal of Environmental Sciences, 21(3), 665–672.
Angel, MLH; Lopez, EP; Granda, MCJ; Usuga, APP. 2020. Identificación de microorganismos biorremediadores de suelos agrícolas del norte de Antioquia para degradación del clorpirifos. Revista Politécnica 16(32):96-110.
Barua, R. C., Kolman, M. A., Aguila, M. S., Zapata, P. D., & Alvarenga, A. E. (2021). Aislamiento e identificación de microorganismos amilolíticos y tolerantes a cianuro de efluentes de la industria almidonera. Revista de Ciencia y Tecnología, 35, 1–10.
Bhardwaj, L; Reddy, B; Nath, AJ; Dubey, SK. 2024. Influence of herbicide on rhizospheric microbial communities and soil properties in irrigated tropical rice field. Ecological Indicators 158:111534.
Canchola, M; Hernández, MR; Luna, RR; Sotelo, MTF; Pérez, MTZ; Roldan, EIC; Cárdenas, JAH; Arvide, MGT. 2021. Contaminantes emergentes: amenaza para la seguridad alimentaria en México. RD-ICUAP :220-232.
Carreón-Abud, Y; Gavito, ME. 2021. Tolerance of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and microorganisms associated to their hyphosphere to aluminum in soil. Scientia fungorum 51.
Cruz-Cárdenas, C. I., Zelaya Molina, L. X., Sandoval Cancino, G., Santos Villalobos, S. D. L., Rojas Anaya, E., Chávez Díaz, I. F., & Ruíz Ramírez, S. (2021). Utilización de microorganismos para una agricultura sostenible en México: consideraciones y retos. Revista mexicana de ciencias agrícolas, 12(5), 899-913.
Dai, XJ; Wang, JL; Xiao, X; Dong, XY; Shen, RF; Zhao, XQ. 2023. Aluminum-Tolerant Wheat Genotype Changes Root Microbial Taxa and Nitrogen Uptake According to Soil pH Levels and Nitrogen Rates. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition 23(1):1360-1373.
de Garcia Fernandez, MB; dos Anjos Leal, O; Júnior, AP; de Oliveira Islabão, L; Silveira, LM; Nogueira, HL; Rocha, JVP; Nascimento, BB; de Oliveira, NL; de Oliveira, M da S. 2023. First assessment of soil mesofauna, microbiota, and humic substances associations in a minesoil revegetated with four grasses in Brazil: An 18-year field study. European Journal of Soil Biology 118:103533.
Dennis, PG; Kukulies, T; Forstner, C; Plisson, F; Eaglesham, G; Pattison, AB. 2023. The effects of atrazine, diuron, fluazifop-p-butyl, haloxyfop-p-methyl, and pendimethalin on soil microbial activity and diversity. Applied Microbiology 3(1):79-89.
Di Lorenzo, R. D., Serra, I., Porro, D., & Branduardi, P. (2022). State of the art on the microbial production of industrially relevant organic acids. Catalysts, 12(2), 234.
Doilom, M., Guo, J.-W., Phookamsak, R., Mortimer, P. E., Karunarathna, S. C., Dong, W., Liao, C.-F., Yan, K., Pem, D., & Suwannarach, N. (2020). Screening of phosphate-solubilizing fungi from air and soil in Yunnan, China: four novel species in Aspergillus, Gongronella, Penicillium, and Talaromyces. Frontiers in Microbiology, 11, 585215.
Ducousso-Détrez, A., Lahrach, Z., Fontaine, J., Lounès-Hadj Sahraoui, A., & Hijri, M. (2024). Cultural techniques capture diverse phosphate-solubilizing bacteria in rock phosphate-enriched habitats. Frontiers in Microbiology, 15, 1280848.
Elhaissoufi, W., Ghoulam, C., Barakat, A., Zeroual, Y., & Bargaz, A. (2022). Phosphate bacterial solubilization: a key rhizosphere driving force enabling higher P use efficiency and crop productivity. Journal of Advanced Research, 38, 13–28.
Elias Estremadoyro, DF. 2022. Impacto de la toxicidad de los residuos sólidos generados por plaguicidas. Revista Kawsaypacha: sociedad y medio ambiente (9):124-139.
Estrada-Gamboa, J., Umaña-Castro, R., Sancho-Blanco, C., & Orozco-Aceves, M. (2023). Aislamiento, identificación y caracterización de cepas bacterianas con potencial de degradación de los plaguicidas clorotalonil y clorpirifos. Uniciencia, 37(1), 481–496.
Fatima, F., Ahmad, M. M., Verma, S. R., & Pathak, N. (2022). Relevance of phosphate solubilizing microbes in sustainable crop production: a review. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 19(9), 9283–9296.
Febles-González, JM; Febles-Díaz, JM; Amaral-Sobrinho, NM; Zonta, E; Maura-Santiago, AV. 2020. Mitos, realidades e incertidumbres sobre la degradación de los suelos Ferralíticos Rojos en Cuba. Cultivos Tropicales 41(3).
Gezahegn, G., Feyissa, T., & Rezene, Y. (2023). Replacement of ammonium nitrate by alternative nitrogen sources in MS medium to enhance ginger (Zingiber officinale Rosc.) in vitro regeneration. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture (PCTOC), 154(1), 89–95.
Gómez-Beltrán MVZ, DA; QF, CP; Villar Argaiz MVZ, D. 2021. Destino ambiental y efectos ecológicos de los tres herbicidas más utilizados en Colombia. CES Medicina Veterinaria y Zootecnia 16(2):47-75.
González-Hernández, JC; Flores-Herrejón, RD. 2022. Debaryomyces hansenii levadura no-convencional y su potencial Biotecnológico. Milenaria, Ciencia y arte (20):18-21.
Goudarzi, T., Tabrizi, L., Alikhani, H. A., Nazeri, V., & Najafi, F. (2023). Phytostimulation properties of indigenous plant growth-promoting bacteria from licorice (Glycyrrhiza glabra L.): Benefits for seed germination and seedling growth. International Journal of Horticultural Science and Technology, 10(1), 53–68.
Guan, N., & Liu, L. (2020). Microbial response to acid stress: mechanisms and applications. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 104(1), 51–65.
Guerrero Ramírez, J. R., Ibarra Muñoz, L. A., Balagurusamy, N., Frías Ramírez, J. E., Alfaro Hernández, L., & Carrillo Campos, J. (2023). Microbiology and Biochemistry of Pesticides Biodegradation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(21), 15969.
Gupta, R; Khan, F; Alqahtani, FM; Hashem, M; Ahmad, F. 2024. Plant growth–promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) assisted bioremediation of Heavy Metal Toxicity. applied biochemistry and biotechnology 196(5):2928-2956.
Gurbanov, R., Kalkanci, B., Karadag, H., & Samgane, G. (2021). Phosphorus solubilizing microorganisms. Biofertilizers: Study and Impact, 151–182.
Haridy, Y., Osenberg, M., Hilger, A., Manke, I., Davesne, D., & Witzmann, F. (2021). Bone metabolism and evolutionary origin of osteocytes: Novel application of FIB-SEM tomography. Science Advances, 7(14), eabb9113.
Hasanuzzaman, M., Mohsin, S. M., Bhuyan, M. H. M. B., Bhuiyan, T. F., Anee, T. I., Masud, A. A. C., & Nahar, K. (2020). Phytotoxicity, environmental and health hazards of herbicides: challenges and ways forward. In Agrochemicals detection, treatment and remediation (pp. 55–99). Elsevier.
Hkudaygulov, G; Chetverikova, D; Bakaeva, M; Kenjieva, A; Chetverikov, S. 2022. Plant growth promoting Rhizobacteria strain role in protecting crops sensitive to sulfonylurea herbicides from stress. Journal of Crop Protection 11(4):525-534.
Hossain, M. M., Rahman, G., Akanda, M. A. M., Solaiman, A. R. M., Islam, M. T., & Rahman, M. M. (2021). Isolation, morphological and biochemical characterization of rhizobacteria from arsenic contaminated paddy soils in Bangladesh: An In vitro study. Asian Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 7(2), 41–55.
Ibrahim, M., Iqbal, M., Tang, Y.-T., Khan, S., Guan, D.-X., & Li, G. (2022). Phosphorus mobilization in plant–soil environments and inspired strategies for managing phosphorus: A review. Agronomy, 12(10), 2539.
Jatuwong, K., Suwannarach, N., Kumla, J., Penkhrue, W., Kakumyan, P., & Lumyong, S. (2020). Bioprocess for production, characteristics, and biotechnological applications of fungal phytases. Frontiers in Microbiology, 11, 493778.
Knyazev, Y. V, Ikkert, O. P., Semenov, S. V, Volochaev, M. N., Molokeev, M. S., Platunov, M. S., Khramov, E. V, Dubrovskiy, A. A., Shestakov, N. P., & Smorodina, E. D. (2022). Superparamagnetic blocking and magnetic interactions in nanoferrihydrite adsorbed on biomineralized nanorod-shaped Fe3S4 crystallites. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 923, 166346.
Kour, D., Rana, K. L., Kaur, T., Yadav, N., Halder, S. K., Yadav, A. N., Sachan, S. G., & Saxena, A. K. (2020). Potassium solubilizing and mobilizing microbes: biodiversity, mechanisms of solubilization, and biotechnological implication for alleviations of abiotic stress. In New and future developments in microbial biotechnology and bioengineering (pp. 177–202). Elsevier.
Kumar, A., Teja, E. S., Mathur, V., & Kumari, R. (2020). Phosphate-solubilizing fungi: Current perspective, mechanisms and potential agricultural applications. Agriculturally Important Fungi for Sustainable Agriculture: Volume 1: Perspective for Diversity and Crop Productivity, 121–141.
Lonkar, K., & Bodade, R. (2021). Potential role of endophytes in weeds and herbicide tolerance in plants. Plant Growth-Promoting Microbes for Sustainable Biotic and Abiotic Stress Management, 227–250.
Li, B; Wang, Y; Hu, T; Qiu, D; Francis, F; Wang, S; Wang, S. 2022. Root-associated microbiota response to ecological factors: role of soil acidity in enhancing citrus tolerance to Huanglongbing. Frontiers in Plant Science 13:937414.
Lu, H., Tan, Y., Zhang, Y., Li, Z., Chen, J., Gao, C., Liu, Y., & Luo, X. (2022). Osteoclastogenesis inhibitory phenolic derivatives produced by the Beibu Gulf coral-associated fungus Acremonium sclerotigenum GXIMD 02501. Fitoterapia, 159, 105201.
Mercl, F., García-Sánchez, M., Kulhánek, M., Košnář, Z., Száková, J., & Tlustoš, P. (2020). Improved phosphorus fertilisation efficiency of wood ash by fungal strains Penicillium sp. PK112 and Trichoderma harzianum OMG08 on acidic soil. Applied Soil Ecology, 147, 103360.
Organización de las Naciones Unidas para la Alimentación y la Agricultura (FAO). (2023). "Biorremediación y microorganismos e invertebrados de los suelos implicados en el ciclo de los elementos nutritivos." Comisión de Recursos Genéticos para la Alimentación y la Agricultura, CGRFA-19/23/9.1.
Parvez, M., Hussain, F., Khan, M., & Sajid, H. (2023). Characterization of phosphate solubilizing fungal endophyte associated with roots of Coriandrum sativum L growing in water stressed soil. Symbiosis, 89(1), 83–94.
Patel, D., & Goswami, D. (2020). Phosphorus solubilization and mobilization: mechanisms, current developments, and future challenge. Advances in Plant Microbiome and Sustainable Agriculture: Functional Annotation and Future Challenges, 1–20.
Paul, RAI; Ammaiyappan, A; Srinivasan, G; Vendan, RT. 2023. Efficacy of Herbicides on Nutrient Uptake of Crop, Weed and Its Impact on Soil Microflora of Irrigated Maize (Zea mays L.). Int. J. Plant Soil Sci 35(1):103-111.
Pérez-Cordero, A., Barraza-Roman, Z., & Martínez-Pacheco, D. (2015). Identificación de bacterias endófitas resistentes a plomo, aisladas de plantas de arroz. Agronomía Mesoamericana, 257–266.
Pileggi, M., Pileggi, S. A. V, & Sadowsky, M. J. (2020). Herbicide bioremediation: from strains to bacterial communities. Heliyon, 6(12).
Raju, N. N., Venkatesan, S. N., Ravi, S. N., Zhou, S., Kulothungan, V. K., & Sankaranarayanan, M. (2024). Microbial Whole-cell Platforms for the Synthesis of Tricarboxylic Acid CycleBased Platform Chemicals. In Whole-Cell Biocatalysis (pp. 123–171). Apple Academic Press.
Rathod, RK; Bhalerao, VP; Margal, PB; Kamble, BM. 2021. Soil Microflora as Influenced by Pre and Post Emergence Herbicide in Sweet Corn Grown in Vertisols. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci 10(01):2794-2801.
Saeed, Q., Xiukang, W., Haider, F. U., Kučerik, J., Mumtaz, M. Z., Holatko, J., Naseem, M., Kintl, A., Ejaz, M., & Naveed, M. (2021). Rhizosphere bacteria in plant growth promotion, biocontrol, and bioremediation of contaminated sites: a comprehensive review of effects and mechanisms. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(19), 10529.
Santana-Flores, A., Sánchez-Ayala, A., Romero-Ramírez, Y., Toledo-Hernández, E., Ortega-Acosta, S. Á., & Toribio-Jiménez, J. (2020). Aislamiento e identificación de bacterias tolerantes y bioacumuladoras de metales pesados, obtenidas de los jales mineros El Fraile, México. Terra Latinoamericana, 38(1), 67–75.
Saygılı, VI; Kadıoğlu, İ; Belgüzar, S; Yanar, Y. 2024. Effect of Some Herbicide (Metribuzin, Pendimethalin and Fluazifop-p-Butyl) on Bacillus cereus and Pseudomonas putida. Journal of Agricultural Faculty of Gaziosmanpaşa University (JAFAG) 40(3):155-162.
Shahid, M., & Khan, M. S. (2022). Ecotoxicological implications of residual pesticides to beneficial soil bacteria: a review. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 188, 105272.
Shahid, M., Khan, M. S., & Singh, U. B. (2023). Pesticide-tolerant microbial consortia: Potential candidates for remediation/clean-up of pesticide-contaminated agricultural soil. Environmental Research, 116724.
Silva, L. I. da, Pereira, M. C., Carvalho, A. M. X. de, Buttrós, V. H., Pasqual, M., & Dória, J. (2023). Phosphorus-solubilizing microorganisms: a key to sustainable agriculture. Agriculture, 13(2), 462.
Singh, U; Walvekar, VA; Sharma, S. 2020. Microbiome as sensitive markers for risk assessment of pesticides. Pesticides in Crop Production: Physiological and Biochemical Action :89-108.
Sotomayor, A., et al. (2022). Consorcios microbianos aplicados en un sistema de producción de plántulas de aguacate (Persea americana Mill.) cultivar 'Criollo'. Revista de la Sociedad Peruana de Ciencias Hortícolas, 26(1), 15-25.
Srinivasulu, M; Maddela, NR; Chandra, MS; Shankar, PC; Rangaswamy, V; Prasad, R. 2024. Microbe-pesticide interactions: Soil enzyme analysis and bacterial degradation of chlorpyrifos. Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology .
Suarez, LY; Riaño, ALR. 2022. Potencial biotecnológico de levaduras identificadas en Norte de Santander. Prospectiva 20(1).
Tian, J., Ge, F., Zhang, D., Deng, S., & Liu, X. (2021). Roles of phosphate solubilizing microorganisms from managing soil phosphorus deficiency to mediating biogeochemical P cycle. Biology, 10(2), 158.
Timofeeva, A., Galyamova, M., & Sedykh, S. (2022). Prospects for using phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms as natural fertilizers in agriculture. Plants, 11(16), 2119.
Varghese, EM; Kour, B; Ramya, S; Kumar, NS; Jisha, MS; Ramakrishnan, B. 2022. Rhizosphere microbe-mediated alleviation of aluminum and iron toxicity in acidic soils. s.l., Elsevier. p. 499-526.
Vera-Morales, M., López Medina, S. E., Naranjo-Morán, J., Quevedo, A., & Ratti, M. F. (2023). Nematophagous fungi: A review of their phosphorus solubilization potential. Microorganisms, 11(1), 137.
Vilchez-Chávez, M., Flores-Santos, J. C., Calderón-Toledo, S., Palma-Villanueva, J., & Zavaleta, A. I. (2024). Bacterias productoras de hidrolasas aisladas de suelos de cultivos de arroz: Caracterización fenotípica y molecular. Manglar, 21(2), 177–182.
Wang, K., Ren, T., Yan, J., Zhu, D., Liao, S., Zhang, Y., Lu, Z., Cong, R., Li, X., & Lu, J. (2022). Straw returning mediates soil microbial biomass carbon and phosphorus turnover to enhance soil phosphorus availability in a rice-oilseed rape rotation with different soil phosphorus levels. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 335, 107991.
Xu, H., Chen, Z., Wu, X., Zhao, L., Wang, N., Mao, D., Ren, H., & Luo, Y. (2021). Antibiotic contamination amplifies the impact of foreign antibiotic-resistant bacteria on soil bacterial community. Science of the Total Environment, 758, 143693.
Zhang, H., Yuan, X., Xiong, T., Wang, H., & Jiang, L. (2020). Bioremediation of co-contaminated soil with heavy metals and pesticides: Influence factors, mechanisms and evaluation methods. Chemical Engineering Journal, 398, 125657.