Efecto de Rhizoglomus intraradices, Stenotrophomonas rhizophila y Fertilizante Sintético Sobre la Morfo-Productividad y Contenido Mineral en Pepino
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.28940/terralatinoamericana.v43i.2226Palabras clave:
bacteriana, colonización, micorrizas, PGPR, rendimiento, rizobacteriaResumen
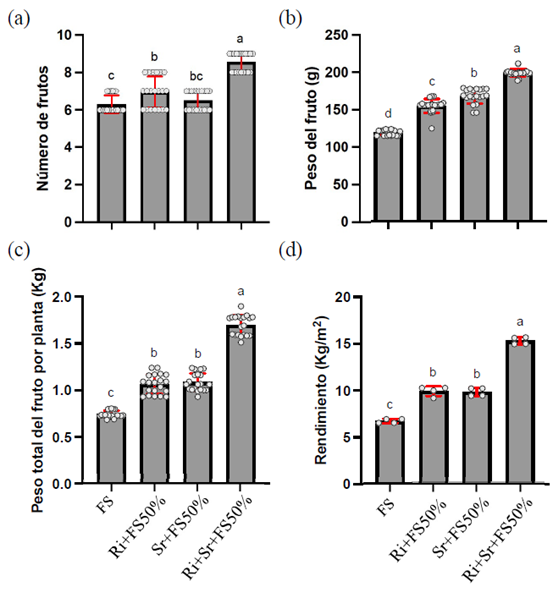
Los hongos micorrízicos arbusculares (HMA) y rizobacterias promotoras del crecimiento vegetal (PGPR) hacen eficiente la aplicación de dosis reducidas de fertilizantes sintéticos, estimulando el crecimiento y la productividad de los cultivos. El objetivo del presente trabajo es evaluar el efecto combinado de Rhizoglomus intraradices, Stenotrophomonas rhizophila y una dosis reducida de fertilizante sintético en la morfo-productividad y contenido mineral de pepino bajo condiciones de invernadero. Un diseño completamente al azar se utilizó con los siguientes tratamientos; Fertilización sintética 100% (FS); R. intraradices + FS 50 % (Ri+FS50%); S. rhizophila + FS 50% (Sr+FS50%) y R. intraradices + S. rhizophila más FS 50% (Ri+Sr+FS50%) utilizando 200 plantas por tratamiento. Se determinó altura (cm), diámetro del tallo (mm), número de hojas y por planta se determinó; número de botones, flores masculinas y femeninas, número de zarcillos, índice de verdor (Iv), número y peso de frutos (g), peso total del fruto/planta (kg), rendimiento (kg m-2), contenido mineral de N, P, K, Ca y Mn en %, unidades formadoras de colonias (UFC) y colonización micorrízica. Los datos fueron procesados a través de un análisis de varianza según el criterio de Tukey a un 95% de confianza. Los resultados indican que las plantas con Ri+Sr+FS50% incremento de forma significativa (P ≤ 0.001) la altura (24.18 cm), diámetro del tallo (6.40 mm), número de hojas (18.35), zarcillos (3.10), flores masculinas (0.4), índice de verdor (256.95), flores femeninas (8.90), número de frutos (8.6) y rendimiento (15.92 kg m-2), en comparación con la aplicación del fertilizante sintético al 100% (FS). El uso de microorganismos benéficos en combinación con una dosis reducida de fertilizantes sintéticos incrementa la productividad del pepino, por lo tanto, puede constituir una alternativa sostenible en los sistemas agrícolas, reduciendo costos de producción y disminuyendo la contaminación ambiental salvaguardando la salud humana y animal.
Descargas
Publication Facts
Reviewer profiles N/D
Author statements
- Academic society
- Terra Latinoamericana
Citas
AbuQamar, S. F., El-Saadony, M. T., Saad, A. M., Desoky, E. S. M., Elrys, A. S., Abd El-Mageed, T. A., Semida, W. M., Abdelkhalik, A., Mosa, W. F., Al Kafaas, S., S., Naser, S., Ibrahim, E. H., Alshamsi, F., M., Mathew, B., T., & El-Tarabily, K. A. (2024). Halotolerant plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria improve soil fertility and plant salinity tolerance for sustainable agriculture - A review. Plant Stress, 12, 100482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stress.2024.100482
Acoltzi-Conde, M. C., Chimal-Sánchez, E., Tovar-Soto, A., & Díaz-Reyes, J. (2024). Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi consortia in six vegetable crops in the Tepeaca Valley, Puebla, Mexico. Terra Latinoamericana, 42. https://doi.org/10.28940/terra.v42i0.1783
Ajibola, O., V., & Amujoyegbe, B. (2019). Effect of seasons, mulching materials, and fruit quality on a cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) Variety. Asian Journal of Agricultural and Horticultural Research, 3(2):1-11. https://doi.org/10.9734/ajahr/2019/v3i229996
Alexander, A., Singh, V. K., & Mishra, A. (2020). Halotolerant PGPR Stenotrophomonas maltophilia BJ01 induces salt tolerance by modulating physiology and biochemical activities of Arachis hypogaea. Frontiers in Microbiology, 11, 568289. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.568289
Aloo, B. N., Tripathi, V., Makumba, B. A., & Mbega, E. R. (2022). Plant growth-promoting rhizobacterial biofertilizers for crop production: The past, present, and future. Frontiers in Plant Science, 13, 1002448. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.1002448
Alvarado-Carrillo, M., Díaz-Franco, A., & Alejandro-Allende, F. (2018). Gallinaza, micorriza arbuscular y fertilización química reducida en la productividad de calabacita y pepino. Revista Internacional de Contaminación Ambiental, 34(2), 273-279. https://doi.org/10.20937/rica.2018.34.02.08
Arcidiacono, M., Pellegrino, E., Nuti, M., & Ercoli, L. (2024). Field inoculation by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi with contrasting life-history strategies differently affects tomato nutrient uptake and residue decomposition dynamics. Plant and Soil, 500(1), 105-127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-023-05995-8
Bhantana, P., Rana, M. S., Sun, X. C., Moussa, M. G., Saleem, M. H., Syaifudin, M., Shah, A., Poudel, A., Bahadur Pun, A., Bhat, M., A., Mandal, D. L., Shah, S., Zhihao, D., Tan, Q., & Cheng-Xiao, H. (2021). Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and its major role in plant growth, zinc nutrition, phosphorous regulation and phytoremediation. Symbiosis, 84, 19-37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-021-00756-6
Bhat, M. A., Mishra, A. K., Jan, S., Bhat, M. A., Kamal, M. A., Rahman, S., Shah, A. A., & Jan, A. T. (2023). Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria in plant health: a perspective study of the underground interaction. Plants, 12(3), 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12030629
Bhunia, S., Bhowmik, A., Mallick, R., & Mukherjee, J. (2021). Agronomic efficiency of animal-derived organic fertilizers and their effects on biology and fertility of soil: A review. Agronomy, 11(5), 823. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11050823
Buzo, F. D. S., Garcia, N. F. S., Garé, L. M., Gato, I. M. B., Martins, J. T., Martins, J. O. M., Souza Morita, P. R., Andrade Silva, M. S., Souza Sales, L. Z., Nogales, A., Rigobelo, E. C., & Arf, O. (2022). Phosphate fertilization and mycorrhizal inoculation increase corn leaf and grain nutrient contents. Agronomy, 12(7), 1597. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12071597
Chandran, H., Meena, M., & Swapnil, P. (2021). Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria as a green alternative for sustainable agriculture. Sustainability, 13, 10986. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131910986
Chen, Y., Wen, H., Pan, J., Du, H., Zhang, K., Zhang, L., & Wang, G. (2021). CsUFO is involved in the formation of flowers and tendrils in cucumber. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 134, 2141-2150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-021-03811-4
Dalai, S., Singh, M., & Soni, S. (2020). Yield and yield traits of cucumer (Cucumis sativus L.) as influenced by foliar application of plant growth regulators. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences, 9(3), 121-126. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2020.903.015
Dhall, R. K., Kaur, H., Manchanda, P., & Sharma, E. (2024). Recent advances in genetics and molecular breeding of parthenocarpic cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) under protected conditions. Euphytica, 220(7), 104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-024-03366-7
Diagne, N., Ngom, M., Djighaly, P. I., Fall, D., Hocher, V., & Svistoonoff, S. (2020). Roles of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on plant growth and performance: Importance in biotic and abiotic stressed regulation. Diversity, 12(10), 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12100370
Elhosieny, A. A. E., Zayed, M. S., Selim, S. M., Yassen, A. M., & Abdel Aziz, N. H. (2023). Stenotrophomonas rhizophila a novel plant-associated bacterium with distinguished PGPRs properties. Arab Universities Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 31(1), 41-50. https://doi.org/10.21608/ajs.2023.159562.1493
Feng, J., Zhang, L., Tang, X., Xia, X., Hu, W., & Zhou, P. (2021). Season and geography induced variation in sea cucumber (Stichopus japonicus) nutritional composition and gut microbiota. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 101, 103838. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2021.103838
Gashash, E. A., Osman, N. A., Alsahli, A. A., Hewait, H. M., Ashmawi, A. E., Alshallash, K. S., El-Taher, A. M., Azab, E. S., Abd El-Raouf, H. S., & Ibrahim, M. F. (2022). Effects of plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) and cyanobacteria on botanical characteristics of tomato (Solanum lycopersicon L.) plants. Plants, 11(20), 2732. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11202732
Ghosh, R., Chatterjee, S., & Mandal, N. C. (2020). Stenotrophomonas. In Beneficial microbes in agro-ecology (pp. 427-442). Academic Press.
Glick, B. R., Patten, C. L., Holquin, G., & Penrose, D. M. (1999) Biochemical and genetic mechanisms used by plant growth promoting bacteria. Imperial College Press, London.
Hernández-Montiel, L. G., Murillo-Amador, B., Chiquito-Contreras, C. J., Zuñiga-Castañeda, C. E., Ruiz-Ramírez, J., & Chiquito-Contreras, R. G. (2020). Morpho-productive response of bell pepper plants biofertilized with Pseudomonas putida and reduced dosage of synthetic fertilizers in greenhouse. Terra Latinoamericana, 38(3), 583-596. https://doi.org/10.28940/terra.v38i3.651
Hnini, M., Rabeh, K., & Oubohssaine, M. (2024). Interactions between beneficial soil microorganisms (PGPR and AMF) and host plants for environmental restoration: A systematic review. Plant Stress, 100391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stress.2024.100391
Ipek, M., Arıkan, Ş., Eşitken, A., Pırlak, L., Turan, M., & Dönmez, M. F. (2021). Effects of some plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) on growth and nutrition of apple Cv.“Braeburn” under high lime soil condition. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 52(5), 432-442. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2020.1849256
Jin, N., Jin, L., Wang, S., Li, J., Liu, F., Liu, Z., Luo, S., Wu, Y., Lyu, J., & Yu, J. (2022). Reduced chemical fertilizer combined with bio-organic fertilizer affects the soil microbial community and yield and quality of lettuce. Frontiers in Microbiology, 13, 863325. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.863325
Kheyri, Z., Moghaddam, M., & Farhadi, N. (2022). Inoculation efficiency of different mycorrhizal species on growth, nutrient uptake, and antioxidant capacity of Calendula officinalis L.: a comparative study. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 22, 1160-1172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00721-8
Khosravi, H., Khoshru, B., Nosratabad, A. F., & Mitra, D. (2024). Exploring the landscape of biofertilizers containing plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria in Iran: Progress and research prospects. Current Research in Microbial Sciences, 100268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crmicr.2024.100268
Kiełkowska, A., & Dziurka, M. (2021). Changes in polyamine pattern mediates sex differentiation and unisexual flower development in monoecious cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Physiologia plantarum, 171(1), 48-65. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.13197
Kudoyarova, G., Arkhipova, T., Korshunova, T., Bakaeva, M., Loginov, O., & Dodd, I. C. (2019). Phytohormone mediation of interactions between plants and non-symbiotic growth promoting bacteria under edaphic stresses. Frontiers in Plant Science, 10, 1368. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01368
Lin, L., Wu, X., Deng, X., Lin, Z., Liu, C., Zhang, J., He, T., Yi, Y., Liu, H., Wang, Y., Sun, W., & Xu, Z. (2024). Mechanisms of low cadmium accumulation in crops: A comprehensive overview from rhizosphere soil to edible parts. Environmental Research, 245, 118054. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.118054
Martínez-Reyes, C. M., Rodríguez-Zaragoza, S., Cabirol, N., Alarcón, A., & Mendoza-López, M. R. (2022). Effect of predation by Colpoda sp. in nitrogen fixation rate of two free-living bacteria. Microbial Ecology, 83, 1026-1035. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-021-01813-9
Mia, M. B., Naher, U. A., Panhwar, Q. A., & Islam, M. T. (2016). Growth promotion of nonlegumes by the inoculation of Bacillus species. Bacilli and Agrobiotechnology, 57-76. En: Islam, M., Rahman, M., Pandey, P., Jha, C., Aeron, A. (Eds.). Bacilli and Agrobiotechnology. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-44409-3_3
Nakano, M., Omae, N., & Tsuda, K. (2022). Inter-organismal phytohormone networks in plant-microbe interactions. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 68, 102258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2022.102258
Naseer, M. A., Zhang, Z. Q., Mukhtar, A., Asad, M. S., Wu, H. Y., Yang, H., & Zhou, X. B. (2024). Strigolactones: A promising tool for nutrient acquisition through arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi symbiosis and abiotic stress tolerance. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 109057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2024.109057
Nasiri, K., Babaeinejad, T., Ghanavati, N., & Mohsenifar, K. (2022). Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi affecting the growth, nutrient uptake and phytoremediation potential of different plants in a cadmium-polluted soil. Biometals, 35(6), 1243-1253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-022-00439-9
Nie, W., He, Q., Guo, H., Zhang, W., Ma, L., Li, J., & Wen, D. (2024). Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi: Boosting crop resilience to environmental stresses. Microorganisms, 12(12), 2448. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122448
Olalde, G. V. M., Mastache, L. Á. A., Carreño, R. E., Martínez, S. J., & Ramírez, L. M. (2014). El sistema de tutorado y poda sobre el rendimiento de pepino en ambiente protegido. Interciencia, 39(10), 712-717.
Onyeaka, H. N., Akinsemolu, A. A., Siyanbola, K. F., & Adetunji, V. A. (2024). Green microbe profile: Rhizophagus intraradices -a review of benevolent fungi promoting plant health and sustainability. Microbiology Research, 15(2), 1028-1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15020068
Parihar, M., Rakshit, A., Rana, K., Tiwari, G., & Jatav, S. S. (2020). The effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculation in mitigating salt stress of pea (Pisum Sativum L.). Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 51(11), 1545-1559. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2020.1784917
Pérez-Pérez, R., Maxime, O., Hernández Ionel, N. M. C, Pérez-Martínez, S., & Del Castillo, D. S. (2020). Aislamiento y caracterización de Stenotrophomonas asociada a rizosfera de maíz (Zea Mays L.). Cultivos Tropicales, 41(2), e03
Phillips, J. M., & Hayman, D. S. (1970). Improved procedures for clearing roots and staining parasitic and vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi for rapid assessment of infection. Transactions of the British mycological Society, 55(1), 158.
Prakash, J., & Arora, N. K. (2019). Phosphate-solubilizing Bacillus sp. enhances growth, phosphorus uptake and oil yield of Mentha arvensis L. 3 Biotech, 9, 1260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1660-5
Riaz, U., Murtaza, G., Anum, W., Samreen, T., Sarfraz, M., & Nazir, M. Z. (2021). Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) as biofertilizers and biopesticides. En: Hakeem, K.R., Dar, G.H., Mehmood, M.A., Bhat, R.A. (Eds). Microbiota and Biofertilizers. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-48771-3_11
Rivas-García, T., Murillo-Amador, B., Reyes-Pérez, J. J., Chiquito-Contreras, R. G., Preciado-Rangel, P., Ávila-Quezada, G. D., Lara-Capistran, L. & Hernandez-Montiel, L. G. (2022). Debaryomyces hansenii, Stenotrophomonas rhizophila, and ulvan as biocontrol agents of fruit rot disease in muskmelon (Cucumis melo L.). Plants, 11(2), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11020184
Rojas-Rodríguez, I. S., Coronado-García, M. A., Rossetti-López, S. R., & Beltrán-Morales, F. A. (2020). Contaminación por nitratos y fosfatos provenientes de la actividad agrícola en la cuenca baja del río Mayo en el estado de Sonora, México. Terra Latinoamericana, 38(2), 247-256. https://doi.org/10.28940/terra.v38i2.642
Saia, S., & Jansa, J. (2022). Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi: the bridge between plants, soils, and humans. Frontiers in Plant Science, 13, 875958. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.875958
Scagliola, M., Valentinuzzi, F., Mimmo, T., Cesco, S., Crecchio, C., & Pii, Y. (2021). Bioinoculants as promising complement of chemical fertilizers for a more sustainable agricultural practice. Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems, 4, 622169. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsufs.2020.622169
Shahwar, D., Mushtaq, Z., Mushtaq, H., Alqarawi, A. A., Park, Y., Alshahrani, T. S., & Faizan, S. (2023). Role of microbial inoculants as bio fertilizers for improving crop productivity: A review. Heliyon, 9(6). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16134
Tang, C., Zhang, Z., Yu, L., & Li, Y. (2023). Research progress of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi promoting citrus growth. Horticulturae, 9(11), 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9111162
Tian, S., Zhu, B., Yin, R., Wang, M., Jiang, Y., Zhang, C., Li, D., Chen, X., Kardol, P., & Liu, M. (2022). Organic fertilization promotes crop productivity through changes in soil aggregation. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 165, 108533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2021.108533
Ulrich, K., Kube, M., Becker, R., Schneck, V., & Ulrich, A. (2021). Genomic analysis of the endophytic Stenotrophomonas strain 169 reveals features related to plant-growth promotion and stress tolerance. Frontiers in Microbiology, 12, 687463. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.687463
Vinolina, N. S., & Sigalingging, R. (2021). Centella asiatica tendril growth of Samosir–Indonesia accession. Earth and Environmental Science, 883(1), 012057. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/883/1/012057
Wu, W. J., Zou, Y. N., Hashem, A., Avila-Quezada, G. D., Abd-Allah, E. F., Wu, Q. S. (2023). Rhizoglomus intraradices is more prominent in improving soil aggregate distribution and stability than in improving plant physiological activities. Agronomy 13(5), 1427. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13051427
Xie, K., Cakmak, I., Wang, S., Zhang, F., & Guo, S. (2021). Synergistic and antagonistic interactions between potassium and magnesium in higher plants. The Crop Journal, 9(2), 249-256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2020.10.00
Yadav, R., Ror, P., Beniwal, R., Kumar, S., & Ramakrishna, W. (2022). Bacillus sp. and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi consortia enhance wheat nutrient and yield in the second‐year field trial: Superior performance in comparison with chemical fertilizers. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 132(3), 2203-2219. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.15371
Zarei, T. (2022). Balancing water deficit stress with plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria: A case study in maize. Rhizosphere, 24, 100621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rhisph.2022.100621
Zhang, Y., Li, Z., Wei, S., Xu, C., Chen, M., Sang, J., Han, Y., Yan, H., Li, Z., Cui, Z., & Ye, X. (2024). Antifungal activity and mechanisms of 2-Ethylhexanol, a volatile organic compound produced by Stenotrophomonas sp. NAU1697, against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cucumerinum. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 72(27), 15213-15227. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.3c09851
Zhao, Y., Ding, W. J., Xu, L., & Sun, J. Q. (2024). A comprehensive comparative genomic analysis revealed that plant growth promoting traits are ubiquitous in strains of Stenotrophomonas. Frontiers in Microbiology, 15, 1395477. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2024.1395477