Ef fect of Bacillus sp. and Trichoderma spp. on the Development of Banana Seedlings (Musa spp. AAA) in the Nursery Stage
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.28940/terralatinoamericana.v43i.2065Keywords:
sustainable agriculture, biocontrol, microbial inoculation, growth promotion, plant progressAbstract
The production of Musa spp. AAA (banana) generates significant foreign exchange globally. For this reason, its cultivation requires tools that ensure healthy and robust plants from the early stages of development. This research aimed to evaluate the ef fect of Bacillus spp. and Trichoderma spp. on the development of banana seedlings (Musa spp. AAA) in the nursery stage. The study was conducted at Quinta Herrera, located at km 23.2 of the Quevedo – Ventanas road. Species of Trichoderma isolated from the Microbiology Laboratory at the Technical State University of Quevedo and microorganisms from two commercial products were studied. The treatments applied at the soil level were: T1: T. asperellum, T2: T. yunnanense, T3: T. asperellum + T. yunnanense, T4: B. subtilis, T5: T. harzianum, T6: B. subtilis + T. harzianum, and
T7: Absolute control. The trials were set up using a completely random design.
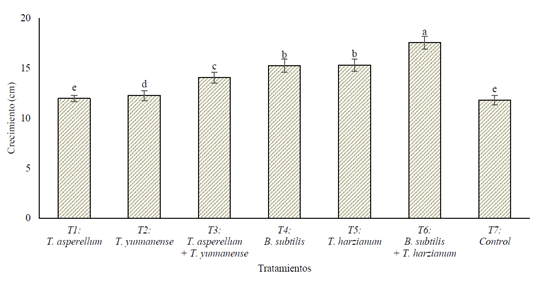
The results showed that, with the combined application of B. subtilis + T. harzianum, the banana seedlings experienced significantly greater growth compared to the other treatments, with an average of 17.54 cm af ter 6 weeks of evaluation, and a pseudostem thickness of 12.50 mm during this period. Leaf emission was similar across all treatments; however, the development of the leaf area was greater in T6, which reached 1517.52 cm² at 20 weeks of seedling age. Finally, the combined application of the two native Trichoderma strains resulted in greater root development, with longer roots (32.93 cm) and consequently higher fresh and dry root weight, with averages of 367.93 g and 145.84 g, respectively. In conclusion, T6 (B. subtilis + T. harzianum) is recommended for improving the development of banana seedlings in the early or vegetative phenological stage under greenhouse conditions.
Downloads
Publication Facts
Reviewer profiles N/A
Author statements
- Academic society
- Terra Latinoamericana
- Publisher
- Mexican Society of Soil Science, C.A.